Download 3DGS Render Addon
Please note: We are making these Blender addons available to you completely for free.:) If you like what we are doing, the best way to support us is to download KIRI Engine app on your phone and consider becoming a KIRI Engine Pro user
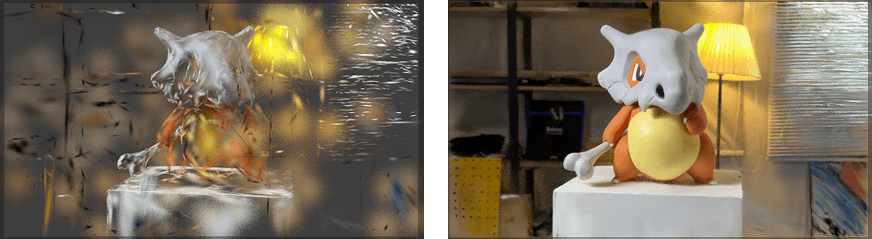
1. Edit Mode Vs Realtime Render

The addon offers 3 distinct modes of working:
- The legacy 'Edit' mode retains edit, modifier and animation functions of earlier versions of the addon. In this mode 3DGS files appear as mesh objects. Performance is slower but the full range of normal mesh edits are available.
- The new (as of version 4.0) Render mode offers real-time and offline rendering of Gaussian Splat objects without the performance constraints of mesh objects.
- The two modes combined offer a full workflow to jump between editing and rendering 3DGS scans
- Using the Mesh-2-3DGS features, mesh objects can be converted to 3DGS .PLY files providing an image texture and associated .MTL are available.
2. Important Notes and Tips
Reading the full documentation is recommended. If you do not have time right now and want to get started immediately, you should at least check these points and the Quick Guides.
- If you are encountering difficulties or want help, try enabling 'Tips' from the bottom of the addon.
- Whenever possible, following a specific workflow (shown in the quick guide and our documentation videos) will result in better performance and faster end results.
- The Mesh-2-GS function requires that .OBJ models are full triangulated and a corresponding texture and .MTL file are in the same folder.
- Only 3DGS .ply files can be imported and used with the addon. If you try to import a non-3DGS .ply (point cloud) file, you may encounter an error such as 'no field of name f_dc_0' or similar.
- In Edit Mode: Once imported, Gaussian Splat scans are converted into a single object with thousands (often millions) of polygon faces. To accurately display the 3DGS object, these faces need to be 'updated' to face the current view/camera.
- In Edit Mode: The process of updating faces can be very performance heavy - especially if done continuously. So, any work that can be done to reduce the number of faces will improve performance.
- In Edit Mode: Faces cannot be updated while in orthographic view. If a 3D viewport in orthographic view is found in the current window – the 3DGS object will turn into a warning cube object. To fix this. Make sure no orthographic views exist and again update faces.
- In Edit Mode: While moving objects or animating and setting up cameras – it is best to display the 3DGS object as a point cloud. When you are all set up – enable camera updates or jump into Render mode
- In Edit Mode: Try using only 1 sample when using HQ Mode if Shadeless shading is enabled.
- In Edit Mode: If you are only using Blender for editing, and not for final renders – you can apply the 3DGS Render modifier immediately after importing.
- In Edit Mode: The export and apply 3DGS transform functions will update 3DGS scale, rotation and colour attributes. 'F_rest' spherical harmonic attribute values will not be updated.
- In Render Mode: If you are rendering multiple 3DGS objects but only some appear in the viewport, jumping between Edit/Render mode and hitting Update can resume correct rendering. The same solution can refresh the scene if no objects are being rendered.
- In Render Mode: If depth sorting is incorrect (wrong parts of the scan appear in front or areas look cloudy) try moving the view with Shift and Middle Mouse.
- 3DGS objects imported with legacy versions of the addon may not work accurately with this/newer versions. Try maintaining addon versions within a projects scope.
3. Quick Guides
Since version 4 of the addon, the addon offers several modes and workflows. We will cover the most condensed version of each workflow here, skipping over more advanced features.
*Video Quick Guides are available on our YouTube channel.
https://www.youtube.com/@BlenderAddon-fromKIRI
Creating a 3DGS object from a mesh object.
- Open the addon N-panel in the 3D Viewport
- Select Mesh 2 3DGS from the Active Menu
- Validate Mesh, Texture and .MTL will check that your file meets the requirements for conversation. This is best left checked.
- Press 'Select .OBJ' to open an import window.
- Select an .OBJ file to convert and press 'Mesh 2 3DGS'
- Wait a few minutes – when the conversion is complete the output folder will open. A new .PLY file will be found in the folder.
Importing a full scene 3DGS scan for making a render.
- Open the addon N-panel in the 3D Viewport. Find the 3DGS Render addon.
- Select Edit from the Active Mode
- Select the Import menu
- Import as Verts (better general performance)
- Keep Create Proxy Object checked.
- Press Import PLY and select your scan.
- After importing, select the object and press Rotate Active To Blender Axis to put the scan the correct orientation for Blender.
*If you do this and plan to export your scan later – read the export warnings about rotation and applying transforms carefully.
- The import object will have Camera Updates set to Disable Camera Updates and will appear as vertices (or faces if imported as faces). If you wish to see colour, experiment with using Show as Point Cloud or Enable Camera Updates, Though disabling these will give best performance during editing.
- Rotate, move and scale your 3DGS object into a desired position.
- Optional performance boost: Add a camera into your scene. Place the camera roughly, just so you can see some parts of your scan when looking through the camera.
With your scan selected and the Active Mode still set to Edit, select the Modifiers menu.
Add a Camera Cull Modifier. If you are not using Blender default camera settings. Adjust the Camera Cull settings or press Auto Set Up to do this automatically.
Clear any floating splat artifacts in front of the camera with the Closer Than distance in the Camera Cull modifier.
Look through the camera and lock the 3D viewport view to the camera view using Camera to View (lock icon in the viewport)
You can now animate your camera as wished. Having the 3DGS shown as vertices, and camera culling enabled can make working much faster.
- Once your scene is ready, you can select Render mode from the Active Mode menu.
- The 3DGS scan should render in real time (unless heavy processing or animation is added)
- From the Render mode, select the Render sub menu. Decide if you want to Render Animation or leave unchecked for a single frame.
It's best to Render a single frame to check settings. If you are happy with the results, you can render a full animation.
If you want to composite the 3DGS scans with mesh elements in the scene, tick Combine With Native Render. Set an output directory and press Render. Rendering will begin offline – to check progress you can open the output directory location to watch image creation. If you are using. Combine With Native Render, temp files will be rendered first, followed by composite images.
Fine editing a 3DGS scan for exporting to external 3DGS viewers.
- Open the addon N-panel in the 3D Viewport
- Select Edit from the Active Mode menu.
- Select Import.
- Disable Create Proxy Object.
- Import as Verts. An import window will open, select your .PLY and press Import PLY. *We will use this import/editing as verts to quickly remove large areas. We will use face import and editing later.
- Use Blender's native edit mode features to remove or edit points. You can also head to the Modifiers menu for non-destructive editing. Modifiers are covered further in their own sections.
- Head to the Export menu
If you have rotated or scaled your object or adjusted colours: use the Apply 3DGS Transforms and Colour button and read the warnings carefully.
- Give your edited object a name and hit Export PLY.
The export function will apply all current rotations and scales to the exported .PLY. All modifiers on the object will be applied– so if you want to continue working or editing, it is best to make a duplicate before exporting.
- We can now reimport the scan as mesh faces for fine edits.
- Repeat the actions to import the scan but this time import as Faces.
- In Edit mode it is easy to see which splats stray from the dense silhouette of an object. You can select and delete these points. If you select a single point in a face, make sure to use Ctrl Numpad+ to select the full face before deleting.
- You can Enable Camera Updates and use Update Active To View or Active Camera functions to better view faces.
- Since we are only editing, not rendering, you can apply the 3DGS render modifier at any point using the Apply Modifiers button in the Active 3DGS Object menu. This can offer a performance boost during editing.
- Once you are happy with your edits, again go to the Export menu and export your scan.
The export function will apply all current rotations and scales to the exported .PLY. All modifiers on the object will be applied– so if you want to continue working or editing, it is best to make a duplicate before exporting.
4. Installation
Important note:
The addon was made with Blender 4.5. The addon should work with Blender 4.3 and above but exceptions may occur.
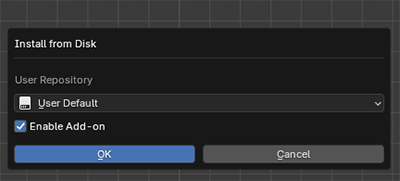
To install the addon make sure you have downloaded the .ZIP file (3dgs_render_by_kiri_engine_version number) .ZIP to your computer.
Drag and drop the .ZIP from a file browser into Blender's 3D viewport.
A confirmation window will appear. Hit okay and the addon will be installed
5. Interface Overview
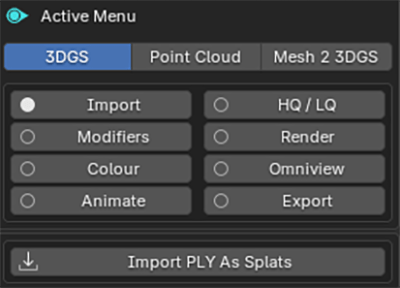
The addon interface is split into three sections. We will look at each section individually in greater detail later:
Active 3DGS Object
Buttons and settings here will affect only the active object, if one is selected.
Active Mode
Here you can select either the Edit or Render modes, or to use the Mesh 2 3DGS function.
Active Sub Menu
Depending on the currently active mode, different sub-menus will be shown.
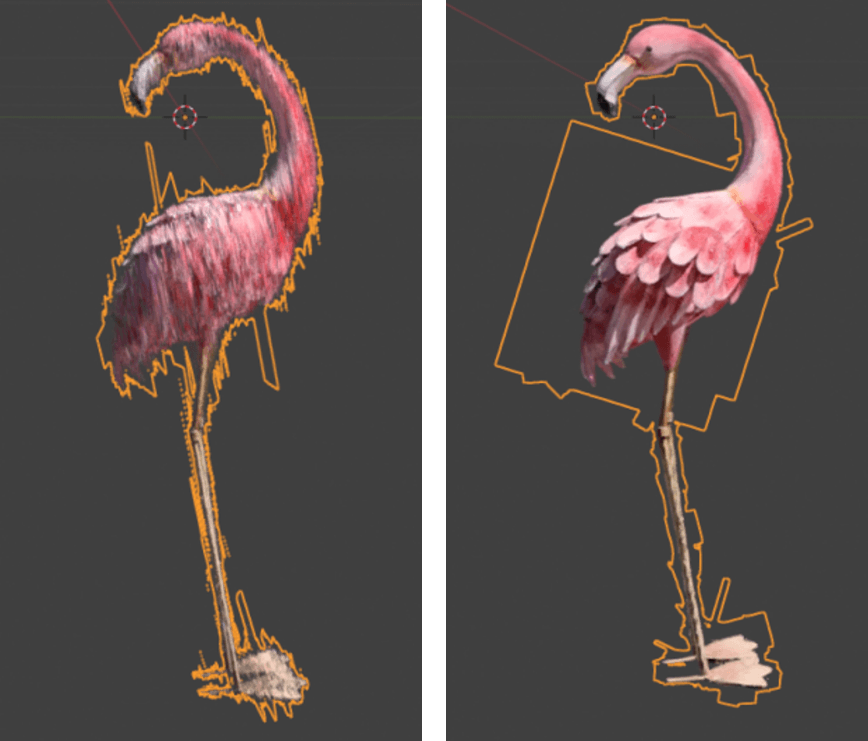

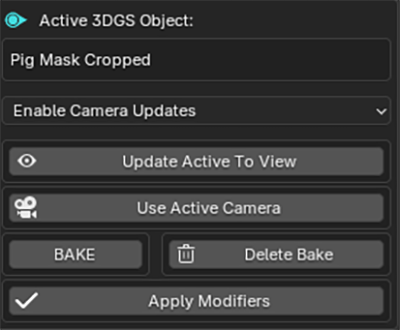
6. Active Object Menu
If a 3DGS object is active, this menu will show offering controls for the active object.
Camera Updates can be enabled or disabled individually for each object.
Immediately after importing, updates for an object are set to disabled.
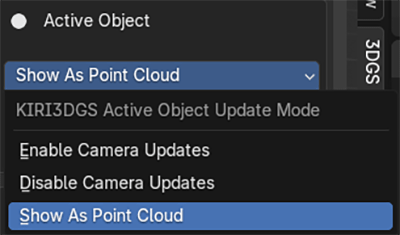
Object updates can be enabled, disabled, or the object can be shown As A Point Cloud

When moving 3DGS objects around in the scene it is recommended to disable updates or Show As A Point Cloud to lighten performance requirements.
If Enable Camera Updates is selected two new options will be available - Update Active To View and Use Active Camera.

-
Update Active To View will update only the active 3DGS object (not the whole scene) to the current view.
Using Active Camera will automatically make the active 3DGS object continually face towards the scene's Active Camera.
Important note:
If you know you are not going to update a 3DGS object again (it may be used in a static camera shot or you are only editing, not rendering) you can apply the 3DGS Render modifier. After doing this the object can no longer be updated to the camera view but performance may be better.
If the active object has Show Point Cloud enabled new options will be shown.

The size of points can be controlled with Point Radius.
The material for points can be specified.
7. Edit Mode - Import
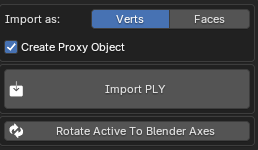
From the Edit mode, Import sub menu you will see the option to Import as: Verts or Faces.
The choice will depend on your needs. For performance considerations, bulk points removal, or mostly using the Render mode – Verts can be a better option.
For very fine detail manual editing, Faces can be better.
Vertex painting is only available to objects imported as Faces.
UV Reset maps can be generated for Faces imported objects with UV Reset enabled.
Create Proxy Object will create the linked Empty object needed for the real time Render mode. If this is disabled on importing the object can be created later (covered in the Render section0)
After pressing Import PLY, a file browser will open.
You can choose a .PLY to import. Depending on the size of the 3DGS scan and your computer specs, you may need to wait for the import to be completed.
Once imported, the new object will have Camera Updates set to Disabled by default. It can be best to enable Show As Point Cloud while working and Enable Camera Updates when ready.
When entering material view or rendered view, be patient while Eevee calculates shaders (it will only do this once).
Since most 3DGS viewers and software do not share the same axes as Blender, you can select the imported object and press Rotate Active To Blender Axes to quickly set it upright.
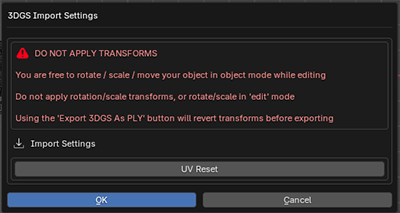
Important note:
Do apply rotation or scale transformations to the 3DGS object.
Updating faces while the viewport is in orthographic mode is not possible. A warning proxy Cube object will show if faces are updated with orthographic views on the screen.
8. Edit Mode - Modifiers

Many of the modifiers on this menu work to reduce the number of points or faces in a 3DGS object. Though they can also be used for animation purposes. It is advised to use Camera Cull at the very least for good performance.
Modifiers can be added with the + icon next to modifier name
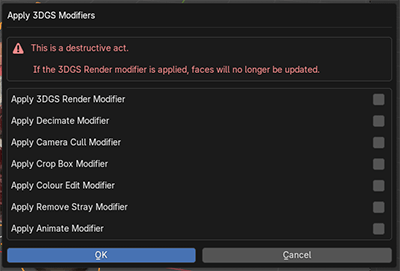
After adding a modifier, the modifier can be toggled on/off in the viewport by clicking its name. A modifier can be applied or removed with the tick and trashcan buttons. If a modifier has previously been applied or removed, it can be re-added multiple times with the + button.

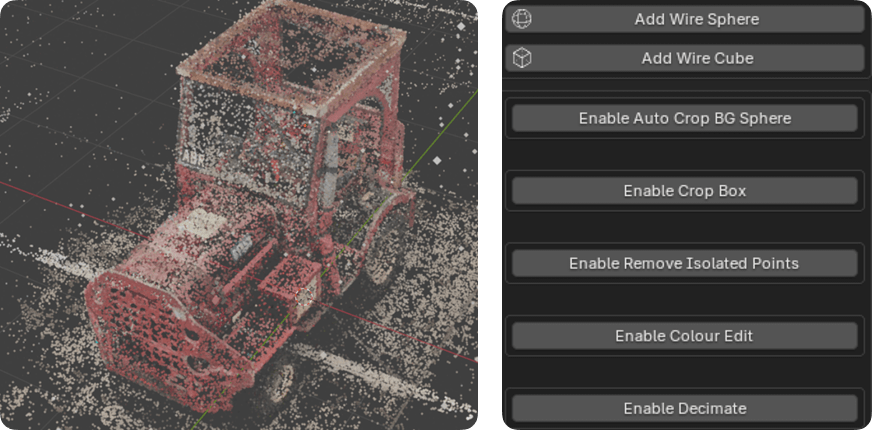
Add Wire Sphere / Cube
This will add a wireframe cube/sphere to the scene. This object will not render and can be used as a target for various modifiers (e.g. crop box)
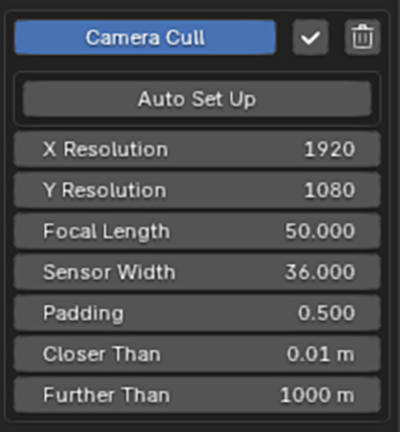
Camera Cull
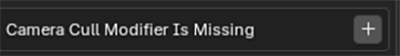
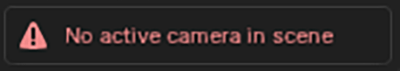
This is often the most important modifier in terms of performance and usability. The modifier will remove faces outside of the camera bounds and by distance to the camera.
An active camera is required to use it – if the modifier is enabled and no active camera is present, a warning will show:
The modifiers settings must match the active camera and scene settings (focal length, render resolution etc) – you can set this up quickly with Auto Set Up.
The distance between the camera bounds and deleted faces is controlled with Padding. It is recommended not to set this a 0 to avoid flickers when moving the camera.
Faces can by distance to the camera using Closer Than and Further Than values.
Decimate
This will remove a percentage of the total number of faces from 0 - 100. The Decimate Seed will change which faces are removed.
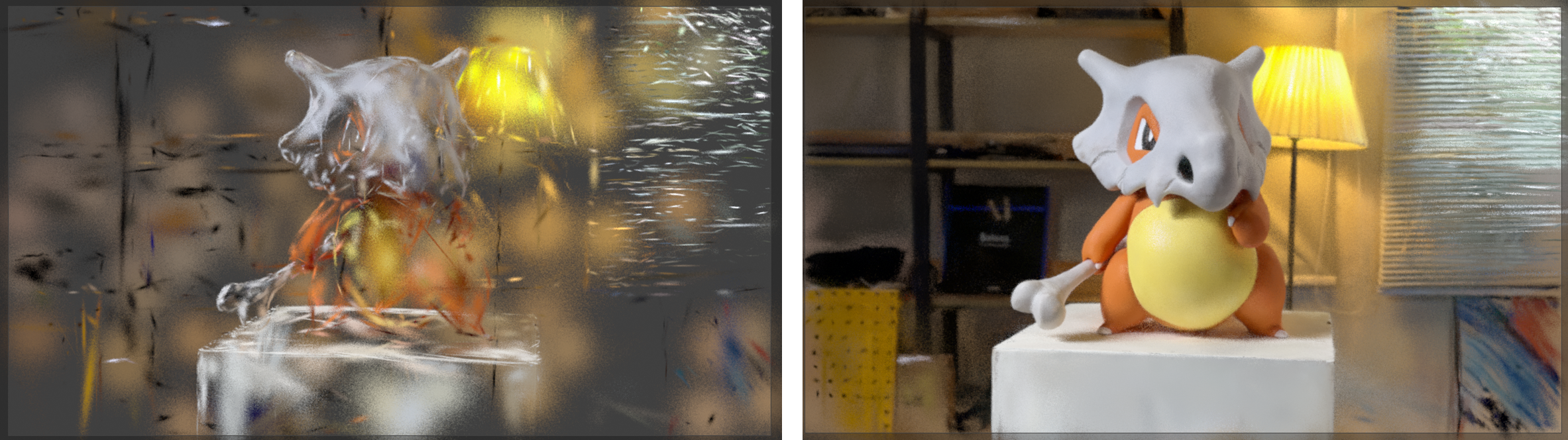

It can be useful to use a high number while working to improve performance, then drop this number during rendering.
Removing any number of faces can be helpful – so a low number like 5% can be used, and the modifier applied to improve performance
The selection of faces that are decimated can be masked by enabling Decimate Masking and selecting a mask object.
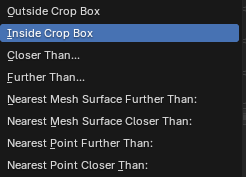
Crop Box
This allows you to specify a crop object or collection and a method of cropping.
Faces or points Inside, Outside or by distance to the crop object/s origin, nearest point or nearest surface can be removed.
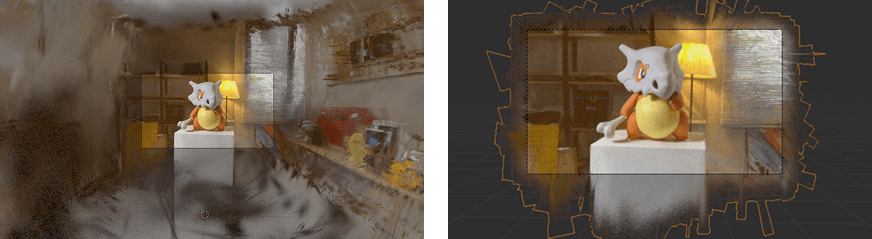
Auto generate crop object will attempt to automatically create a crop object based on the most focussed cluster of points. This is a great way to quickly remove background points.
Pressing the button will give several options.
The Mode is an under-the-hood preset for how quickly or aggressively you want to remove points. Quick is usually advised.
If you are getting bad results, changing the Filter Epsilon to a higher number is the first course of action. The epsilon value is relative to the total scale of an object – hence the need to vary it for different scans. The higher the value, the less points will be removed (more points in the final object).
The Filter Min Points can usually be ignored unless you're an advanced user.
The function deletes points based on points sparseness or proximity to its neighbours. Filter Min Points determines the number of points required to be within a found cluster to keep them save (deleting sparse versus tightly grouped points. A lower number would preserve more points and vice versa.
Filter Fast Mode and sometimes speed the process up at the cost of accuracy.
By default, the new object is composed only of points. Create Convex Hull Object will create a mesh object encapsulating the remaining points
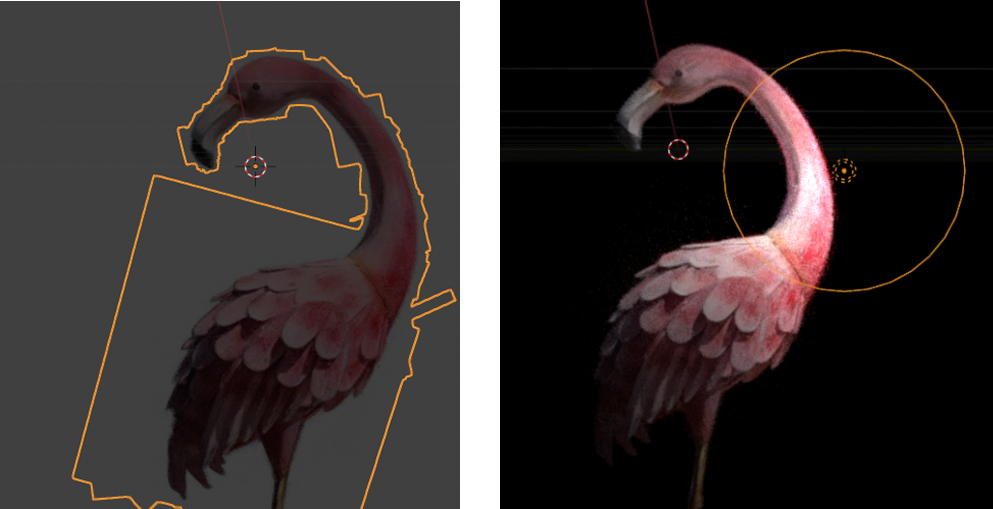
Original 3DGS Object:

Auto Crop Object – Epsilon 0.03 (Default)
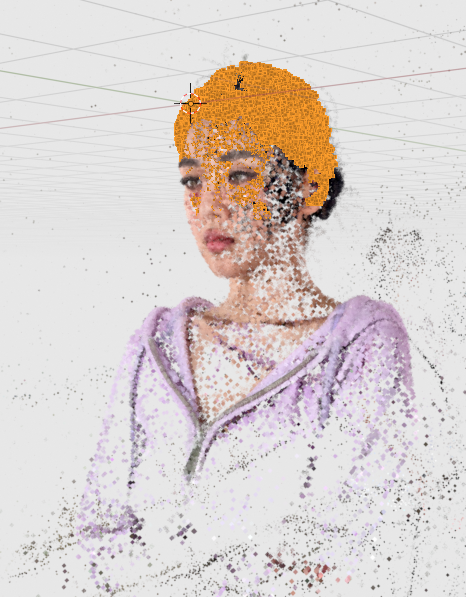

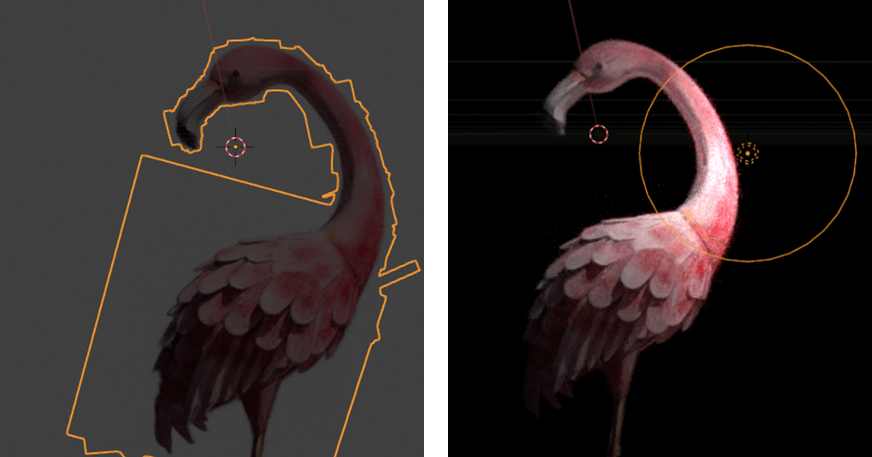
Auto Crop Object – Epsilon 0.08

Auto Crop Object – Epsilon 0.08 – Create Convex Hull Object enabled
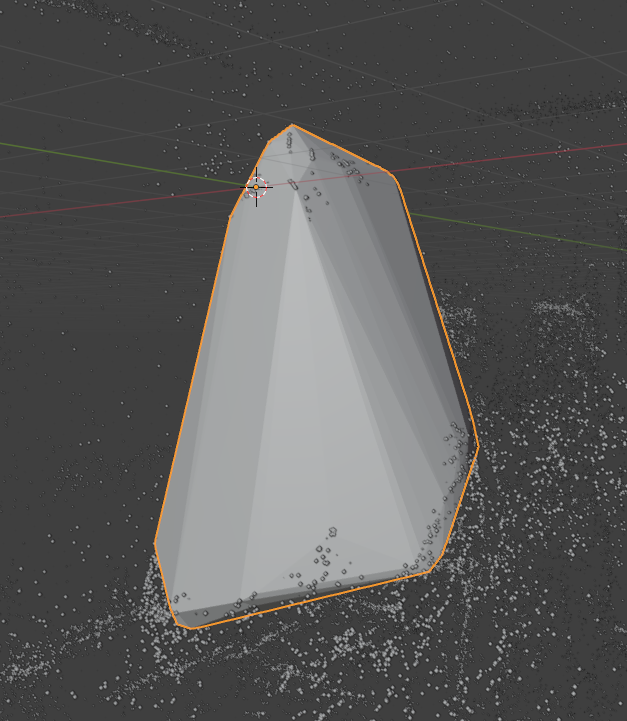
The created object can be specified as the Crop Object within the Crop Box modifier.
Default point cloud objects work well with the Nearest Point Closer/Further Than option.
Convex Hull objects work well with the Inside/Outside Crop Box option.
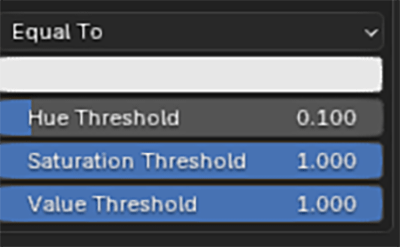
Colour Edit
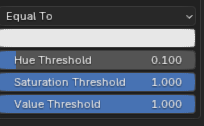
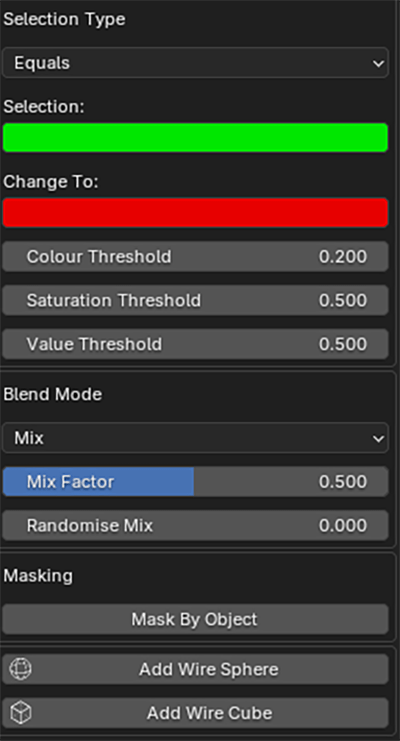
Faces are removed according to their colour. A colour selection and a removal method can be set. Faces can be removed if their colour is Equal To, Not Equal To, Darker Than or Brighter Than the selection colour
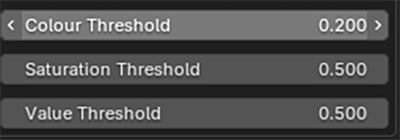
The colour selection can be finetuned with hue, saturation and value thresholds.
The selection of faces that are affected by the Colour Edit modifier can be masked by enabling Colour Edit Masking and selecting a mask object.
Important note:
Due to Blender limitations – red values may be very difficult to select.
Remove By Size
This will remove faces based on native 3DGS scale attributes
You can remove faces Bigger or Smaller Than Threshold and set a Threshold value.
The selection of faces that are affected by the Remove By Size modifier can be masked by enabling Remove By Size Masking and selecting a mask object.
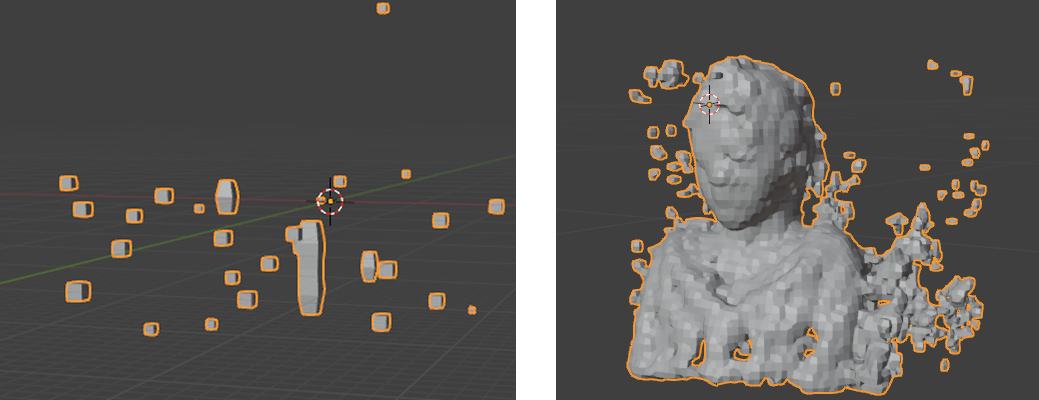
Convert To Rough Mesh
This will turn a 3DGS object into a rough manifold mesh – useful as a Crop Box object, for shadow casting or other mesh specific operations.
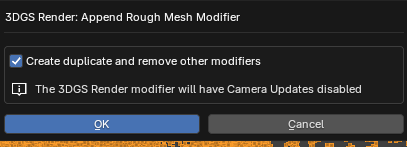
After pressing the + icon to add the modifier you are given some options.
Enabling Create duplicate and remove other modifiers will create a duplicate object of your currently active object. The new object will have all modifiers applied and be given the Convert To Rough Mesh modifier. If this option is disabled, the active object will be given the modifier and it's Camera updates will be set to Disable Camera Updates. The mesh conversion will not work correctly with camera updates enabled.
Once added your object may look like a sparse collection of cubes, or a defined mesh depending on the input.
The mesh quality can be adjusted with the Voxel, Simplify and Smoothing settings.
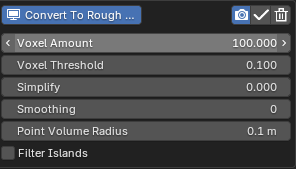
To isolate the largest mesh island component, you can use Filter Islands. By adjusting the Island Threshold value, you can remove mesh islands bigger or smaller than the threshold.
After filtering islands and adjusting voxel values.

Adjust Attributes
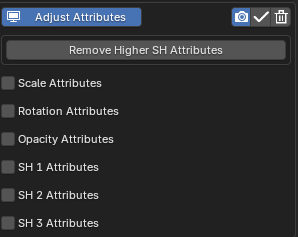
The internal data used to give Gaussian Splats their metallic, reflective and special appearances is stored as various attributes such as f_rest_0, f_rest_1 etc.
There names mean very little to the average user, and most programs do not offer the ability to edit this data easily. The Adjust Attributes modifier allows you to easily play with this data to see what experimental results you can get.
SH and Opacity attribute changes are only visible in the higher quality Render mode- hence, this modifier is the only one which can be easily edited while in Render mode, with the parent/mesh 3DGS object selected. Scale and rotation attributes changes
Attribute values to change can be enabled and the math operation to affect their current values can be specified.
Since 3DGS Attributes can react extremely to small changes, is it best to make very slight edits. Large value edits can cause freezes or a Blender crash.

Importantly for the Rotation Attributes, you are adjusting the internal rotation values, not the normal rotation values of the faces displayed in the Edit mode.
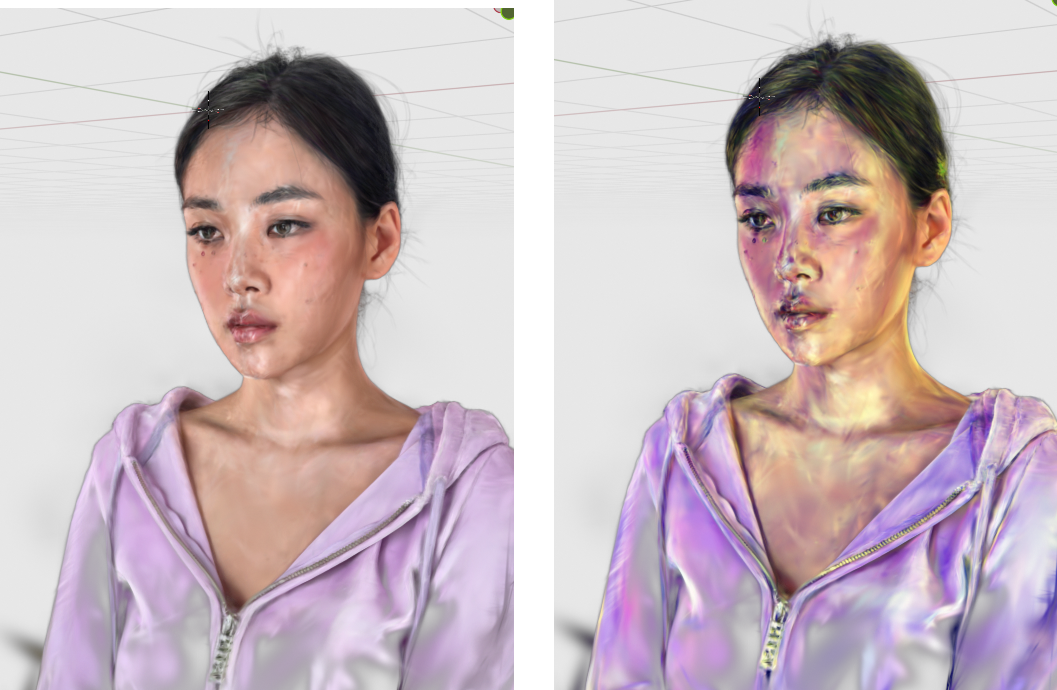
After attributes have been adjusted on a parent/mesh object – use Update Scene while in render mode to see the effects of any SH or Opacity changes.
Before and after editing SH3 values

9. Edit Mode - Colour
The Colour menu allows you to easily paint, texture and perform basic colour edits on the active 3DGS object. These edits are all exportable and will be written to the exported .PLY file.
Shadeless
At the top of the Colour menu, you can toggle Shadeless lighting on/off. When shadeless is enabled, the object will not react to the lights or World lighting in the scene. If shadeless is disabled, the object will use a Principled BSDF shader and react to lighting.

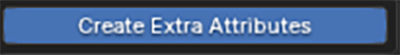
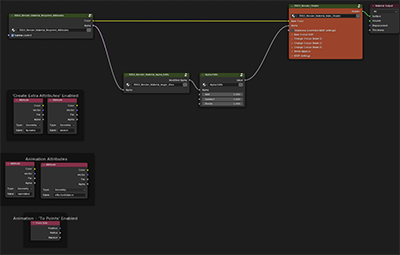
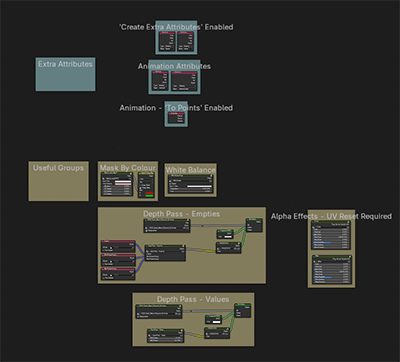
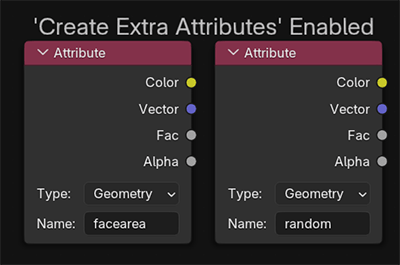
Create Extra Attributes
For advanced users, greater control can be gained by manipulating the material directly within the shader editor – where named attributes can be used to control values.
Enabling Create Extra Attribute will create some extra, useful attributes inside the material's node tree such as face area and random per point.
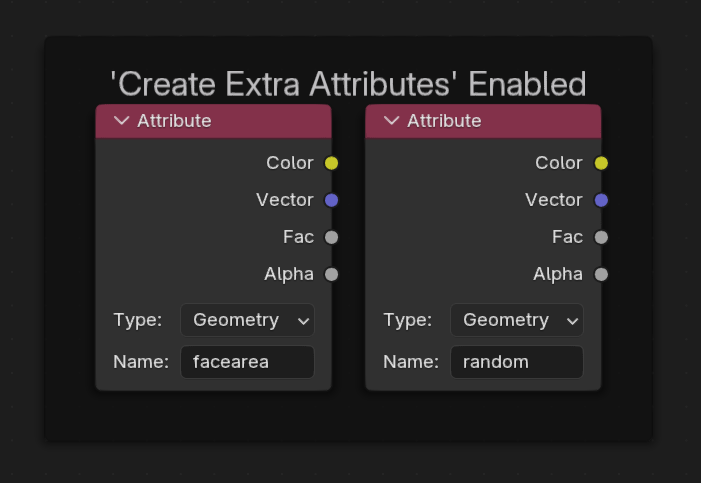
Creating extra attributes can be costly performance-wise, so this is disabled by default.
We will cover these attributes more in the shader section.
Basic Adjustments
Under extra attributes we have controls for basic colour edits including brightness, contrast, hue and saturation. Their controls are self-explanatory.
Active Colour Menu
There are many colour functions available within the addon, so the colour menu has its own sub-menu: Active Colour Menu. From here you can select which advanced colour operations to perform. If an advanced colour operation is enabled, that option will be highlighted red on the menu.
Important note:
The apparent resolution of any colour edits will be determined by the 3DGS objects number of splats and splat scale etc
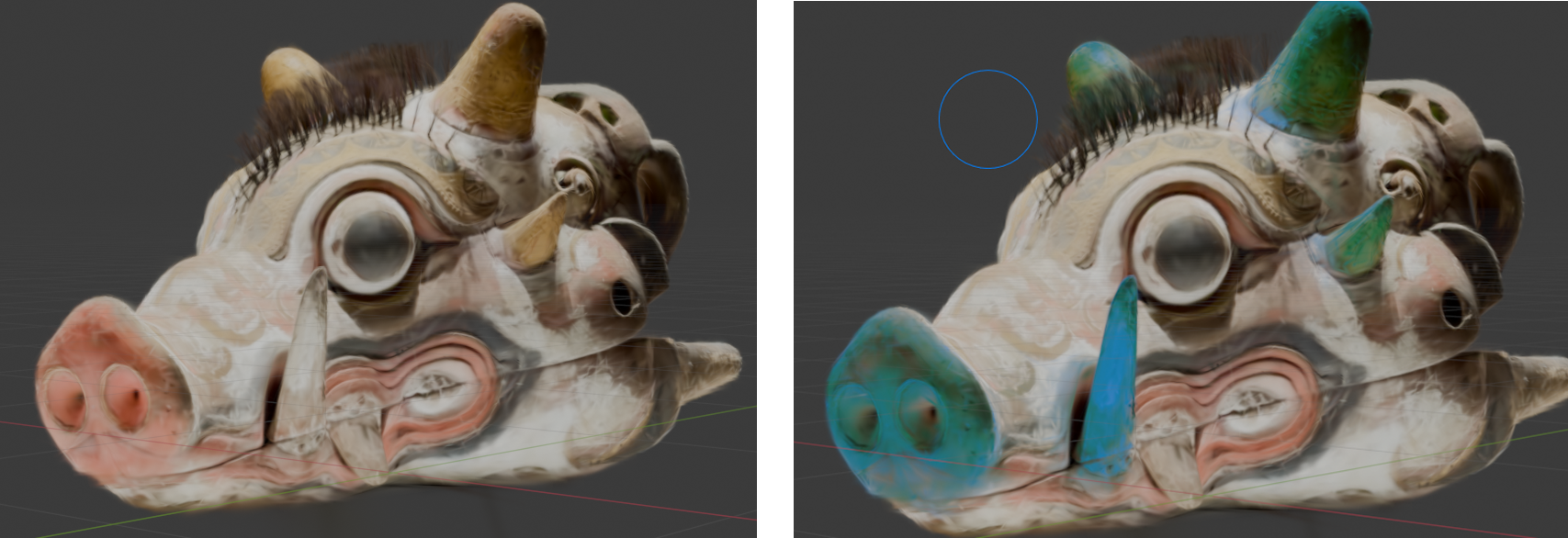
Selective Colour Adjustments
It is possible to target a specific colour within your object and replace that colour with another colour, and specific blend mode.
This can be performed up to 3 times using different colours. They are listed on the Active Colour Menu as Selective 1, Selective 2 and Selective 3

Inside each selective adjustment, you can specify a colour selection/target and a colour to change to/blend with.
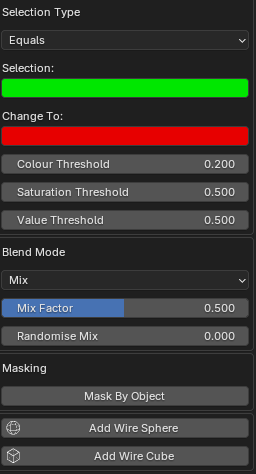
You can adjust the selection with the hue, saturation and value threshold sliders.
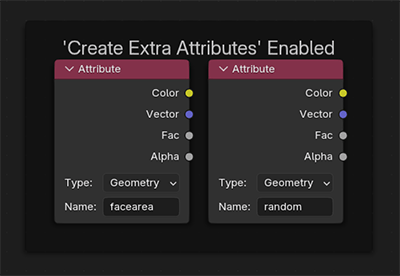
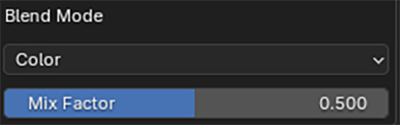
You can control the replacement method and strength with the Blend Mode and Mix Factor. A more natural look can be achieved with the Randomise Mix.
The selection of faces that are affected by selective colour edits can be masked by enabling Mask by Object and selecting a mask object.
Vertex Paint
3DGS objects can be painted directly using Blenders native vertex painting features.
*Objects imported as Verts cannot be vertex painted.

Vertex painting can be enabled first by toggling Enable vertex Painting.
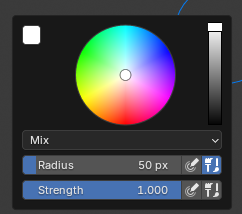
Pressing Start Painting will enter vertex paint mode. The brush settings for painting are available from Blender's default vertex paint menus. Either by right clicking or from the top header.
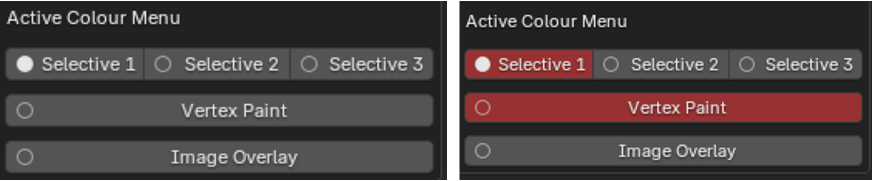
Faces or points currently selected in Edit mode can be masked with the mask toggles.

If you are unhappy with your painting and want to return to the original state – Reset Paint will revert all paint edits to their original form.
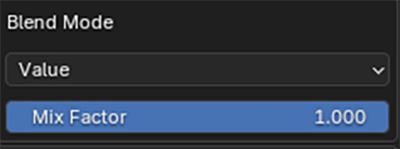
The style of colour replacement and replacement strength can be controlled with the Blend Mode and Mix Factor controls.

All paint edits can be masked by enabling Mask by Object and selecting a mask object.

Image Overlay
Image Overlay allows you to use an image texture to affect the splat colours.
The feature can be enabled by toggling Enable Image Overlay.
If a desired image texture is already present in the Blend file, it can be selected from the Image ID search bar. Or the folder button can be used to select and import an image directly.
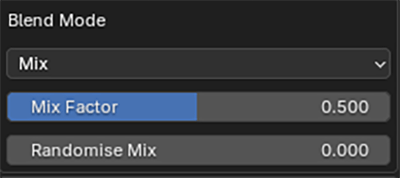
The style of colour replacement and replacement strength can be controlled with the Blend Mode and Mix Factor controls.

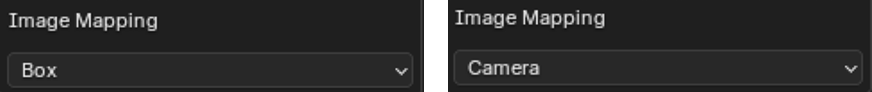
The type of mapping used by the texture can be set using Image Mapping. Box and Camera use the box and camera mapping methods standard to Blender shader nodes.
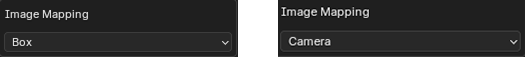
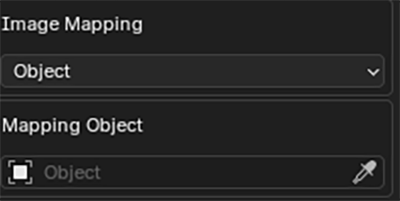
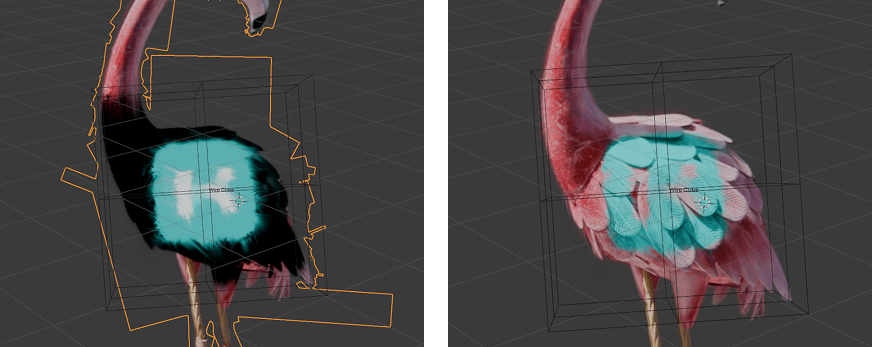
If Object mapping is selected. An object can be chosen to adjust the texture placement. The Add Wire Sphere/Cube buttons can be useful for this. Note that the objects local Z axis is considered the 'forward' axis.

Object mapping can be used in conjunction with Masking to overlay logos or text images.
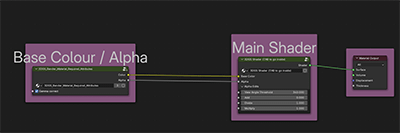
10. Edit Mode - Materials and Extra Attributes
All imported 3DGS objects are given the KIRI_3DGS_Render_Material

This material can be replaced, renamed, copied or altered as the user wishes. All colour edits shown on the addon interface are produced by Geometry Nodes attributes.
This means that separate 3DGS objects can have varying materials.
If a 3DGS object's material contains the Base Colour / Alpha and Main Shader groups – addon colour edits should propagate.
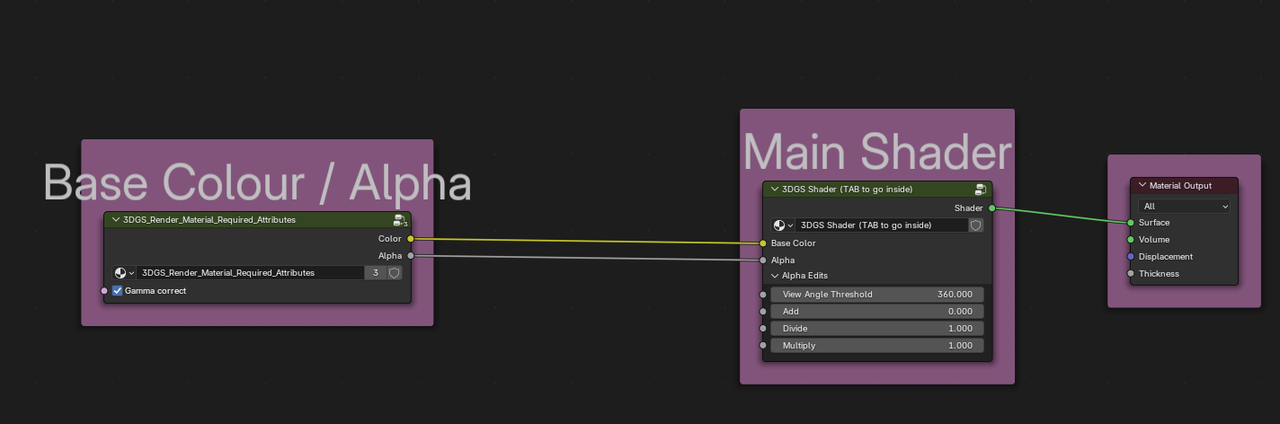
Beginner Blender users can stick to making colour edits using the addon interface.
For Advanced users several extra nodes and groups are included for fun.
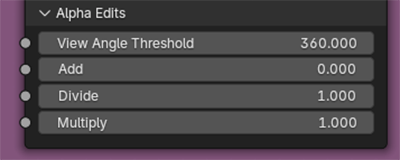
The Alpha Edits controls on the main shader can produce some stylish animation result – and are often more performance friendly than directing editing the geometry with modifiers.
The View Angle Threshold will make the faces transparent at set viewing angles.
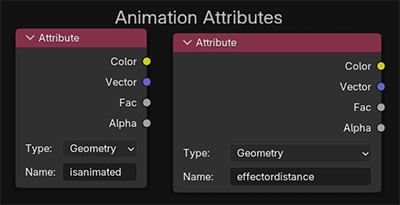
If Create Extra Attributes is enabled in the Shader menu, a face area and a random-per-face attribute can be used.
If the Animate modifier is enabled, isanimated and effector distance attributes are available

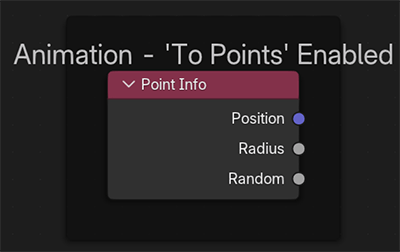
If Animate modifier is enabled and the To Points preset is used, the Point Info node can be useful.
Mask By Colour for selective colour editing, and White Balance groups are also included.
Important note:
Colour changes made inside the shader are not exportable. Only changes made by the addon and Geometry Nodes will be exported.
11. Edit Mode - Animate
This Animate modifier comes preloaded with presets and settings to quickly create stylised motion graphics renders using your 3DGS objects.
Important note:
Using the shader and alpha edits or shader displacement is often a more performant way to animate very dense meshes
As updating faces is already a highly performance intensive task, it is extremely recommended that you:
- Use and apply as many modifiers as possible to reduce face counts.
- Work on an isolated object/separate part of your scan, rather than a full 3DGS scene.
- Use the Decimate Animated slider to reduce the number of faces affected by the animation
Animation effects can be Global (applied to the whole object), or by distance to a selected object or collection.
If Effect By Object or Effect By Collection is chosen, a distance threshold will appear and anything below this will be animated.

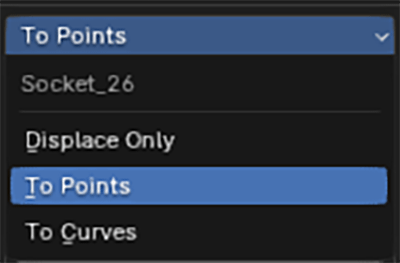
There are 3 modes of animation, Displace Only, To Points and To Curves.
Each mode supports some of the following effects:
Noise Displacement – displaces faces based on the standard Blender Noise texture

This is available in all animation modes.
There are controls for the Noise Strength and Noise Scale.
The Time Evolution Multiplier will change the noise seed as the timeline is played. This is performance intensive so set to 0 as default.
Voronoi Displacement – displaces faces based on the Blender Voronoi Noise texture
This is available in all animation modes. The results are more chaotic looking than the standard Noise Displacement.
There are controls for the Noise Strength and Noise Scale.
The Time Evolution Multiplier will change the noise seed as the timeline is played. This is performance intensive so set to 0 as default.
Pixelate – points of each face are snapped to Blender's world grid, forming grid patterns
This is available in all animation modes.
There are controls for the Pixelate Mix and Grid Scale.
To Points – animated faces will turn into points
This is available in the To Points animation mode.
Any animated faces will turn into points. All displacements/pixelate will contribute to point positions.
To Curves – animated faces will turn into curves
This is available in the To Curves animation mode.
Any animated faces will turn into curves. All displacements/pixelate will contribute to curve positions.
12. Edit Mode - HQ / LQ
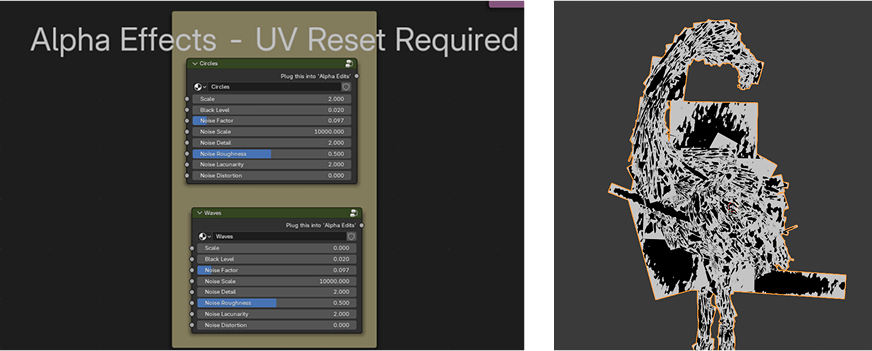
Material transparency has two modes in Blender: dithered and blended.
In the addon and documentation we refer to dithered materials as LQ (low quality) and blended as HQ (high quality).
LQ mode can appear quite grainy and will give flickering artifacts in renders.
HQ mode is much smoother and should remove flickering artifacts. Due to Blender material limitations, LQ mode supports depth of field, but HQ does not.
By default, the HQ Mode menu will show a warning if no camera is in the scene.
HQ mode requires an active camera. After adding a camera, you will see more options.

Each material on your active object will be shown and can be toggled between HQ and LQ modes.
Important note:
HQ mode is more performance intensive while working in the viewport. You should work in LQ Mode, and enable HQ Mode to preview final renders.
When using HQ Mode, you can often get acceptable results using 1 sample, which makes rendering much faster.

If you have multiple 3DGS objects that intersect each other, you will need to enable the Objects Overlap? button.
After enabling Objects Overlap? – a new button will be shown – Generate HQ Object, pressing this will do a few things:

Move all current 3DGS objects (we will consider them LQ objects) into a new collection named 3DGS_LQ_Objects (we will refer to these as LQ Objects).
These LQ objects will be hidden from view and render (while in HQ Mode).
A new object will be created, KIRI_HQ_Merged_Object (we will refer to this as HQ Object). and placed into a new collection, 3DGS_HQ_Object.
This new object is a merged instance of all objects in the 3DGS_HQ_Object collection.
While the HQ Object exists, toggling between LQ and HQ mode will toggle visibility and render for either all objects in the LQ collection, or the HQ object.
Important note:
If you have generated an HQ Object but want to continue editing/placing your LQ objects – switch to LQ mode, make your changes, then switch back to HQ mode.
Don't move LQ objects from the 3DGS_LQ_Objects collection while using an HQ object.
13. Edit Mode - Export
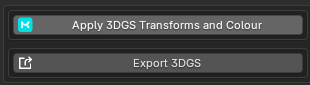
Important note:
As stated in the addons tips. If you have rotated or a scaled 3DGS objects and applied those transforms using Blender native Apply Scale / Apply Rotation, the 3DGS attributes will not be updated correctly and the object can no longer be exported to other 3DGS apps.
The export function for both the 3DGS and Point Cloud menus will update 3DGS attributes correctly before exporting.
Note that Spherical Harmonic / F_Rest values are not updated, so the export is functional only for programs in which f_rest values are arbitrary (e.g. Supersplat)
The export function will apply all modifiers on the object before exporting, so it is advised to make a copy of your objects before hitting export.
Only one toggle and one check box are shown on the export menu.
If enabled, the Reset Origin switch will send your object back to the world origin before exporting.
The Export 3DGS or Export Points For 3DGS buttons will apply all modifiers, colour edits and 3DGS Transforms on the active object. An export window will then be opened. Select your file path, name your object and hit Export PLY.
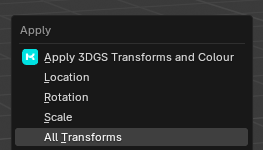
Rotation and scale transforms should not be applied to 3DGS objects using Blender's native 'Ctrl+A….Apply Rotation/Scale'. Doing this breaks the 3DGS data.
If you want to apply the transforms correctly while editing – there will be a new button added to the Ctrl+A and Export menus. Apply 3DGS Transforms and Colour.
Pressing this will apply all 3DGS modifiers on the object, Including the 3DGS Render modifier.
The 3DGS transforms values will be updated correctly -which the exception of the f_rest values.
After two separate 3DGS objects have their transforms applied – they can be merged and exported.
14. Render Mode
Render - Proxy Empty Objects - Create
After editing and placing 3DGS objects in the scene, we can preview them in real time using the Render mode.
For an object to appear in Render mode – the imported mesh PLY needs to have an associated Empty object. The Empty object can be scaled, moved and rotated to control the Gaussian Splats appearance.
By default, these Empty objects are created on importing a PLY if Create Proxy Object is checked.

If this was unchecked or somehow the Proxy Empty was deleted or corrupted a new one can be created from Render – Create. The mesh 3DGS object can be selected and pressing Create Proxy From Active will create a new Empty object.
Render - Scene Updates / Clean Up
The scene is automatically updated when entering Render mode – reflecting any geometry changes made in Edit mode.
The scene can also be updated with the Update Scene button.
Updates can occur a Single Time, or at Intervals. Using Intervals is generally not advised unless you have very small, lightweight scans.
If at any point you want to stop rendering in the scene you can use Stop Viewport Rendering on the Render – Clean Up menu. Empties can also be cleared by checking Delete All Proxy Empties.
Render - Rendering
The results seen in the viewport while in Render mode, can be rendered offline from the Render - Render sub menu.
By default, a single frame will be rendered, but animations can be rendered by checking Render Animation.
A Color Pass, Depth Pass or both can be rendered by ticking their check boxes.
An Active Camera must exist in the scene, and an Output directory must be specified for the Render button to become active. Once pressed, the scene will begin rendering offline. You can view progress of the render by opening your output directory folder.
If you want to combine the results of the 3DGS render with mesh objects in the scene, you can enable Combine With Native Render. Render progress will again be visible in the output folder, but to perform the necessary image compositing temp versions of the scene will first be rendered.
15. Mesh 2 3DGS

Important note:
Only Windows currently supports Mesh 2 3DGS, more OS may be added in the future.
Your .OBJ mesh must be triangulated and have a corresponding colour image in .JPG or .PNG formats as well as an accurate .MTL file. All files must be in the same folder and the names inside the .MTL file must be correct.
From the Mesh 2 3DGS menu we can see the above warnings, a toggle for Validate Mesh, Texture and .MTL, and a button for Select .OBJ.
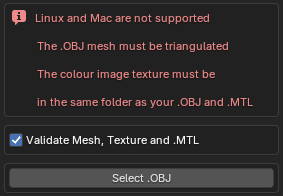
The Validate Mesh, Texture and .MTL toggle will attempt to check that your mesh and associated files meet the requirements to perform the conversion.
It is recommended top leave this checked, but if you think the addon is falsely flagging a correct mesh and file structure, you can disable it to skip this check.
Pressing Select .OBJ will open an import window. From here, select your .OBJ file.
Important note:
It can be useful the first time you use this function to open the System Console from Window….Toggle System Console, to check that the process is running.
Once the process is complete, the output folder will open and a new .PLY file be present. It will be named with the base mesh name, plus _mesh2gs suffix

16. Extra Resources

The buttons at the bottom of the addon can launch web browsers with the add-on's written and video documentation, KIRI addon page or Super Hive Market page.